Policy formulation, planning, etc. regarding activities to achieve SDGs carried out by the Japanese government, developing country governments, development assistance organizations (international organizations, bilateral aid organizations, etc.), local governments, civil society, universities and private companies, etc. We support project implementation and evaluation work and make recommendations. So far, the main areas of focus have been governance and gender, including health, peacebuilding and DX.


| Project Title | Advisor for Social Protection and Care of Vulnerable Children and Families |
| Country | Republic of Tajikistan |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency(JICA) |
| Period | March, 2025 to March,2027 |
| Position |
Individual Expert |
| Type of Service |
Technical Cooperation |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Tajikistan is a young country, with approximately 44% of its population under 18 years old and 36.5% under 14 years old (2020). Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the country experienced a rise in poverty rates, which had previously been steadily declining. To build a resilient society capable of withstanding various domestic and international shocks, Tajikistan aims to further strengthen its social protection system. In 2022, the Government of Tajikistan approved the "Strategy for the Development of Population and Social Protection of the Republic of Tajikistan (SDSPP2040)" to address challenges in social protection, designating the Ministry of Health and Social Protection (MOHSPP) as the leading national institution for the implementation of SDSPP2040. This advisor will support the Ministry of Health and Social Protection of Tajikistan in accelerating the implementation of the national strategy on community and family-based social protection and care for vulnerable children and families (including children and families with disabilities). |
| Project Title | The Project for the Promotion of Collaboration between BMGF and JICA |
| Country | India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Indonesia, ASEAN (ACPHEED) and other Asian countries |
| Client | Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) |
| Period | November 2024 – September 2025 |
| Type of Service |
Investigation |
| SDGs |
.jpg) |
| Outline | In the past, the Gates Foundation and JICA have collaborated project-level in Pakistan and Nigeria to combat infectious diseases. In addition, They are aligning their own strategies at the global level such as the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (GFATM), the GAVI Alliance, and the Global Financing Facility (GFF) for maternal, newborn and child health. |
| Project Title | Information gathering and verification survey for the introduction digital health technology for the promotion of global cluster strategy |
| Country | Bhutan, Honduras, Nepal, Laos |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency(JICA) |
| Period | October. 2024-September. 2026 |
| Position |
Deputy Chief |
| Type of Service |
Investigation and resarch |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | In recent years, the use of digital technology in the health sector has been actively promoted. It is not limited to the easy and rapid sharing of records and reports through digitalization, but has also spread in various fields, such as telemedicine, tele-education, medical care support using AI, and policy support using big data. |
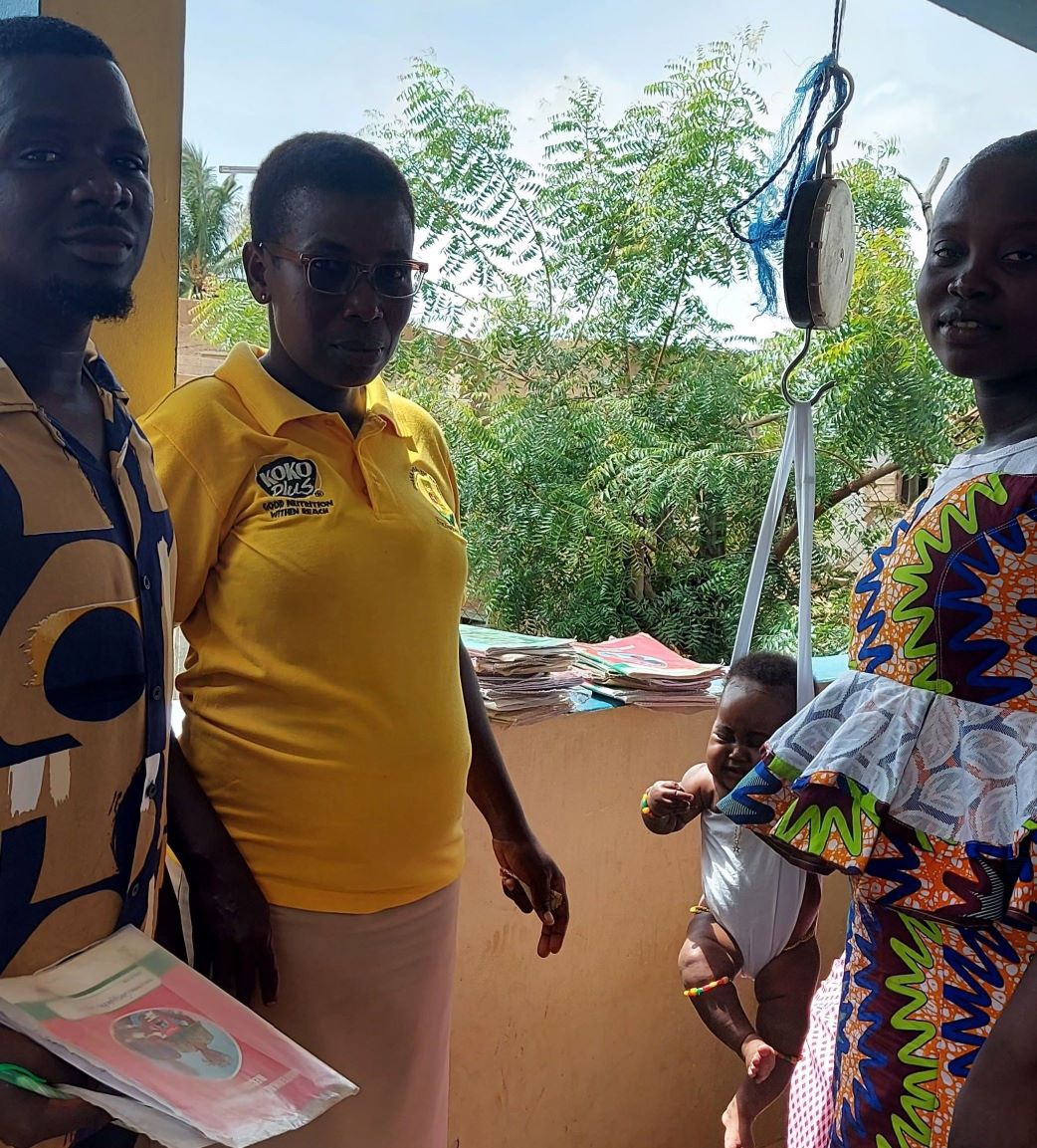
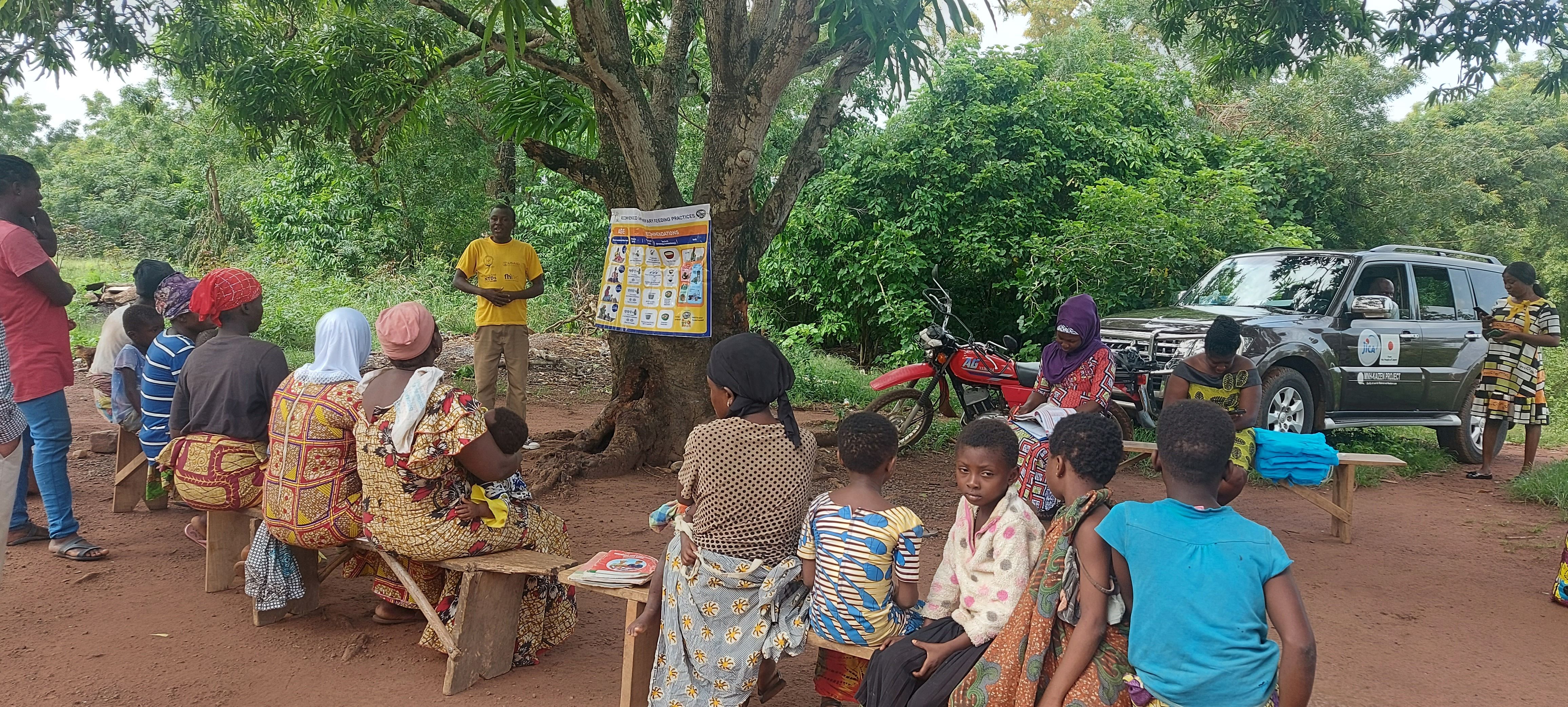
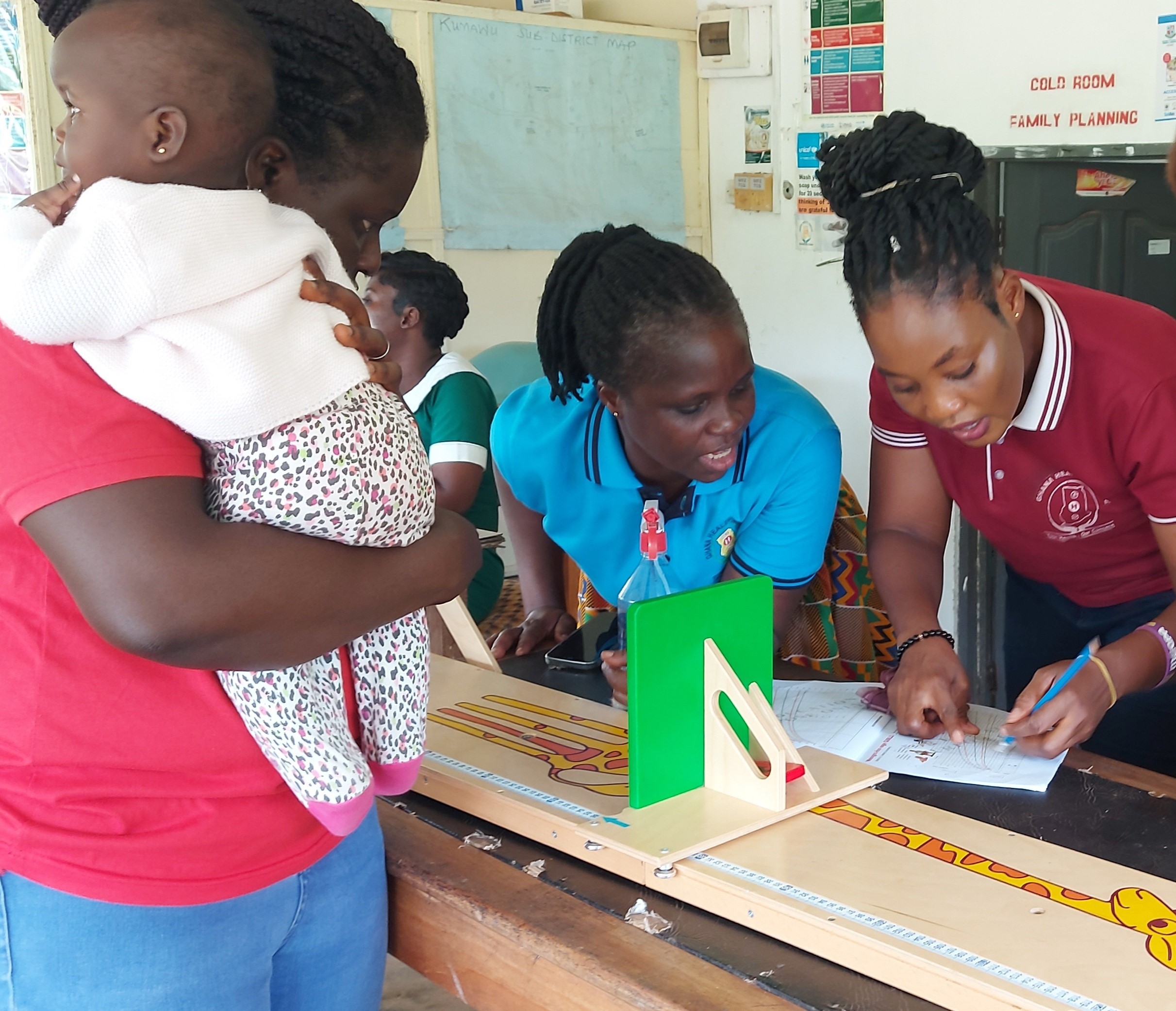
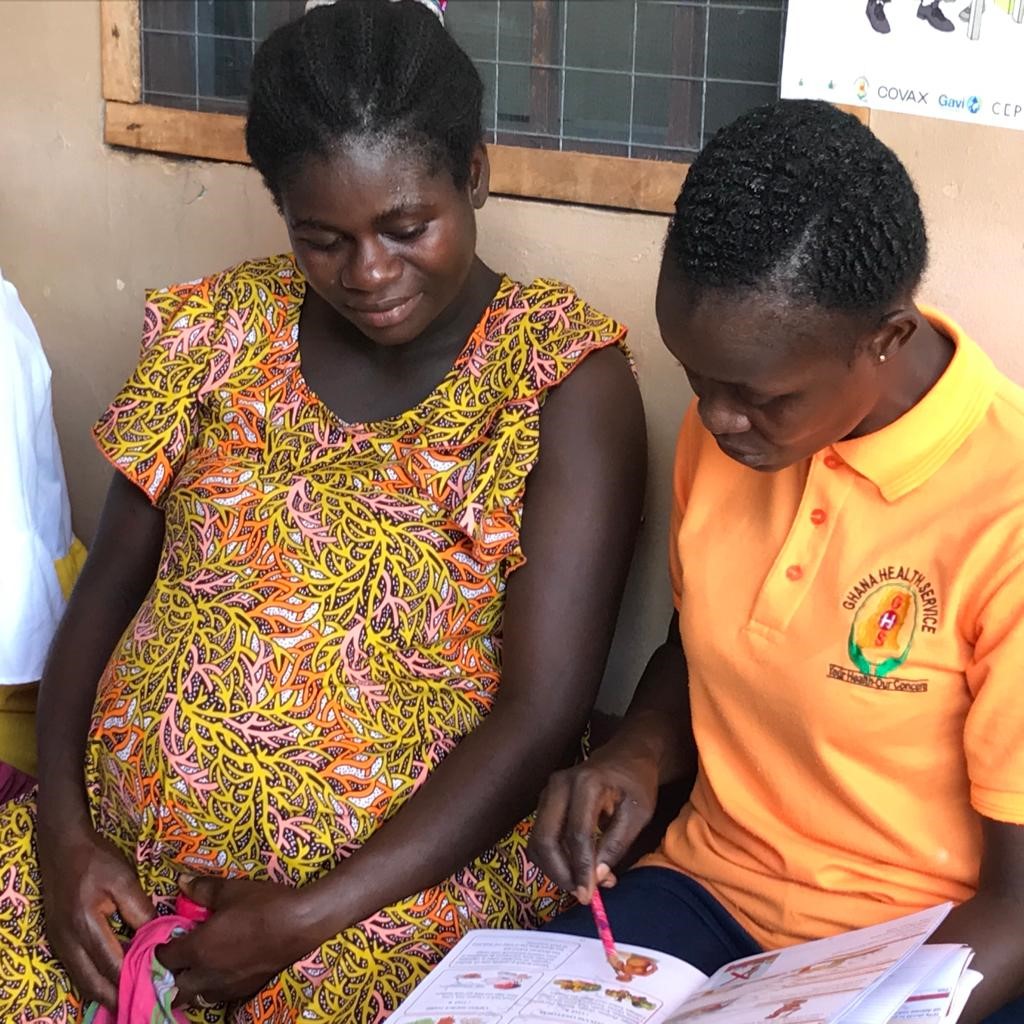
| Project Title | Quality of Care for Maternal and Newborn Health with Focus on 5S-KAIZEN-TQM Country( second phase) |
||||||||
| Country | Ghana |
||||||||
| Client | Ghana Ministry of Health (GMOH), Ghana Health Service (GHS) |
||||||||
| Period | March, 2024 to July,2027 |
||||||||
| Position |
Project expert on Maternal and Child Health |
||||||||
| Type of Service |
Technical Cooperation | ||||||||
| SDGs |
 |
||||||||
| Photo |
|
||||||||
| Outline | The Project on the Quality of Care for Maternal and Newborn Health with Focus on 5S-KAIZEN-TQM is expected to improve the quality of MCH service at health facilities as the second phaseThe project has will be implemented in 4 regions such as Ashanti, Northern, Greater Accra and Volta. The outputs will consist of 1) Ghana Quality of Care Standards with focus on maternal, newborn and child health are practiced, 2) Quality improvement activities at national, regional, district, sub-district and community levels of the health system are practiced with the implementation of 5S-KAIZEN-TQM, 3) Capacity of quality improvement of continuum of care for maternal and newborn is strengthened in Ashanti Region. 4) Referral and counter referral of mothers and newborns are practiced and strengthened by system improvement from CHPS to Regional level. Ultimately this project is expected to contribute to improvement of care for mothers and newborns in targeted regions. The PSD staff will be responsible for mainly Output 3. Thus, PSD staff will implement the technical cooperation on activities to strengthen the capacity of health personnel on the quality of continuum of care for pregnant women and newborns using maternal and child health record book. Concretely, the training on nutrition counselling and respectful care, and subsequent monitoring &supervision will be under its responsibility. *Universal Health Coverage (UHC) is where “everyone can receive adequate quality health care services, when needed, at a manageable cost.” |
||||||||
| Project Title | Data Collection Survey on Health Service Delivery in Mombasa County, Kenya |
| Country | Kenya |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency(JICA) |
| Period | December 2022 - March 2023 |
| Position |
Chief of project and hospital management |
| Type of Service |
Investigation and resarch |
| SDGs |
 |
| Photo |
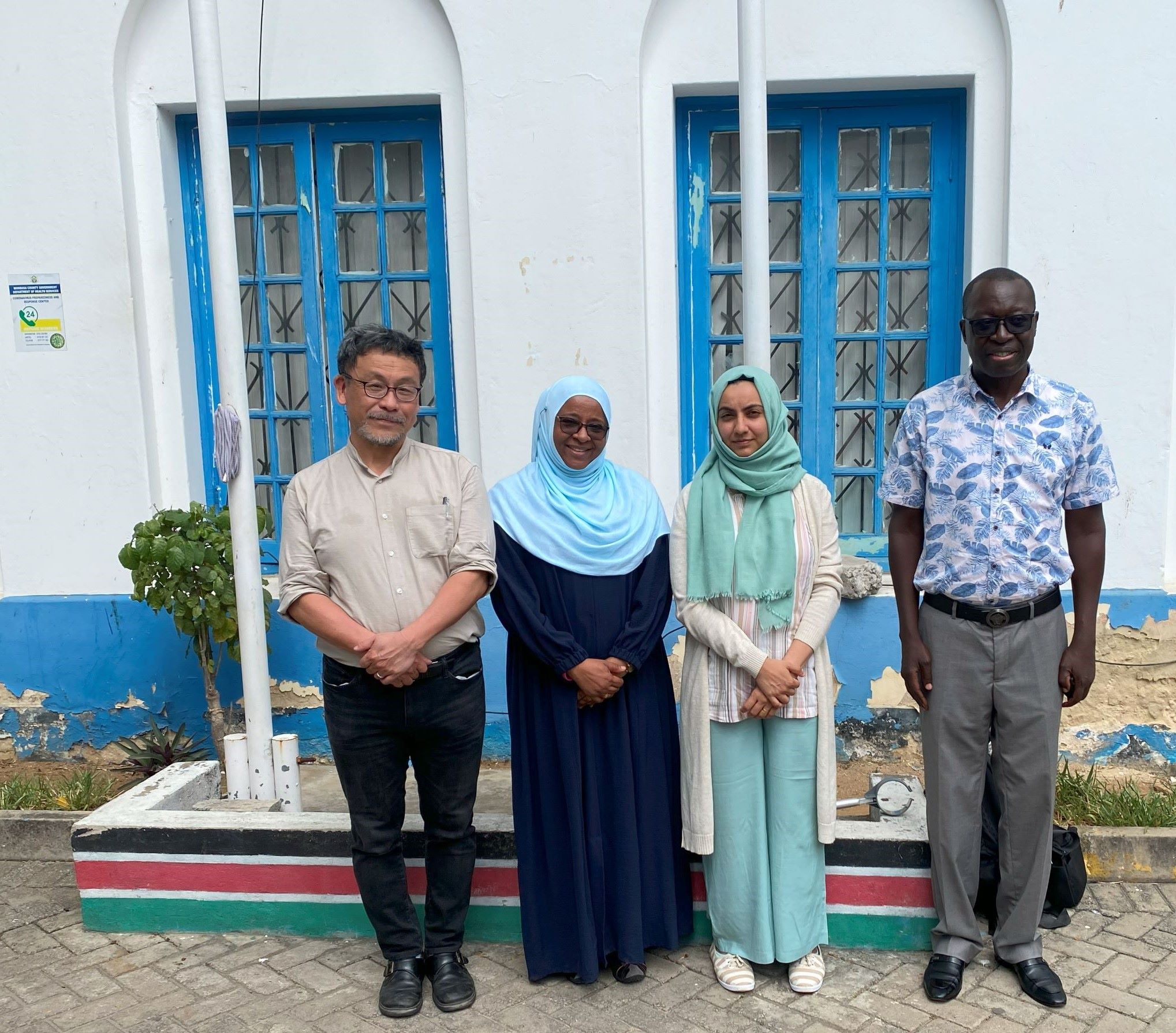 |
| Outline | Under the national development plan, called Kenya Vision 2030, the Kenyan government aims for Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by 2030. However, since the decentralization in 2013, the central Ministry of Health has been responsible for policy-making, guideline development, and management of national referral hospitals, while each local government has been tasked with providing healthcare services. Consequently, regional disparities in health service delivery systems and access to services have emerged. |
| Project Title | Additional Component Of The Project For Capacity Development Of ICU Using Telemedicine Under COVID-19 Pandemic |
||||||||
| Country | Indonesia |
||||||||
| Client | Japan International Coordination Agency |
||||||||
| Period | October 2022 - April 2024 |
||||||||
| Position |
Telemedicine Model Planning and Operation 2 |
||||||||
| Type of Service |
Technical Cooperation | ||||||||
| SDGs |
 |
||||||||
| Photo |
|
||||||||
| Outline | Although healthcare indicators have shown gradual improvement in Indonesia, the under-five mortality rate, number of hospital beds and medical personnel per capita have not reached WHO standards. Furthermore, the disparity in healthcare between urban and rural areas is evident. Therefore, it is an urgent matter to fairly distribute medical resources and services to achieve the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) challenge. The Ministry of Health in Indonesia has formulated a health strategy plan called RENSTRA 2020-2024 as part of the e-health strategy (2017). This healthcare strategy aims to expand the number of telemedicine-capable facilities from 67 in 2020 to 335 by 2024, by strengthening telemedicine and expanding the infrastructure for digitizing healthcare service. In light of this situation, Japan International Cooperation Agency has collaborated with counter-partner hospitals, University of Indonesia Hospital and Hasanuddin University Hospital to contribute to strengthening telemedicine technology in the field of ICU. This project is aiming to enhance telemedicine for diagnostic support and knowledge and skill sharing in not only the ICU, but also in ophthalmology and obstetrics. The project is expected to reduce health disparities between urban and rural areas. |
||||||||
| Project Title | Quality of Care for Maternal and Newborn Health with Focus on 5S-KAIZEN-TQM Country |
||||||||
| Country | Ghana |
||||||||
| Client | Ghana Ministry of Health (GMOH), Ghana Health Service (GHS) |
||||||||
| Period | June, 2022 to January,2024 |
||||||||
| Position |
Project expert on Maternal and Child Health |
||||||||
| Type of Service |
Technical Cooperation | ||||||||
| SDGs |
 |
||||||||
| Photo |
|
||||||||
| Outline | The government of Ghana has been striving to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC)*. So far, there are some improvements in the rate of delivery by the skilled childbirth attendants, attendance of antenatal and postnatal clinics, immunization rate of children and so forth. Consequently, the mortality rate of mothers and children decreased by half from 1990. Despite these positive results, under-five and maternal mortality ratios remain still high at 52 per thousand live births, 310 per 100,000 live births (the 2017 Ghana Maternal Health Survey) respectively. In 2016 National Healthcare Quality Strategy (NHQS) 2017-2021 was formulated. To implement this strategy, Quality Management Department was established in GMOH in 2018, and the guideline for National Healthcare Quality Strategy was launched by Ghana Health Service (GHS) in 2019. It is acknowledged that there are needs of more training and financial support for full-scale implementation of this guideline. Therefore, the Government of Ghana requested JICA for a project, namely Quality of Care for Maternal and Newborn Health with Focus on 5S-KAIZEN-TQM. It is expected to improve the quality of MCH service at health facilities through the project. This project has been implemented in 4 regions such as Ashanti, Northern, Greater Accra and Volta. The activities will be 1) Ghana Quality of Care Standards with focus on maternal, newborn and child health are practiced, 2) Quality improvement activities at national, regional, district, sub-district and community levels of the health system are practiced with the implementation of 5S-KAIZEN-TQM, 3) Capacity of quality improvement of continuum of care for maternal and newborn is strengthened in Ashanti Region. 4) Referral and counter referral of mothers and newborns are practiced and strengthened by system improvement at regional to CHPS level. Ultimately this project is expected to contribute to improvement of care of mothers and newborns in targeted regions. *Universal Health Coverage (UHC) is where “everyone can receive adequate quality health care services, when needed, at a manageable cost.” |
||||||||
| Project Title | Strengthening the Technical Capacity Development of the Local Government Service (Records Management and Fixed Assets Management) The 3rd Phase |
| Country | Ghana |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) |
| Period | May 2022 - October 2023 |
| Position |
Advisor (Local Government Capacity Development) |
| Type of Service |
Independent Expert Service |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | The government system in Ghana has central government institutions and its local government, which structures regions and districts (Metropolitan, Municipal and District). The Office of the Head of the Local Government Service (OHLGS) under the Office of the President has once developed operational manuals both of records management and fixed assets, however, they are not implemented in local government institutions. Many institutions do not completely store important records and update fixed assets registers periodically. |
| Project Title | Health System Governance and Management |
| Country | Eswatini |
| Client | The World Bank |
| Period | Nov. 2021-June 2023 |
| Position |
Design and Formulation of Facility-level Service Profiles |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Eswatini’s health challenges include an ongoing COVID-19 epidemic, a large HIV epidemic, persistently high maternal and child mortality, a large and unaddressed burden of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), and malnutrition. Shortcomings in the health system foundations – particularly in health financing, governance and management and service delivery - have led to poor quality of care (QoC), a significant barrier to universal health coverage (UHC) attainment. |
| Project Title | The Project for Promotion of Nepal National Building Code Compliance for Safer Building Construction |
| Country | Nepal |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) |
| Period | June 2021 - May 2025 |
| Position |
Building Information Management |
| Type of Service |
Technical Cooperation Project |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Ministry of Urban Development implemented “the Project for Assessment of Earthquake Disaster Risk for the Kathmandu Valley,” which revealed more than one million evacuees would be forcefully evacuated due to tremendous number of building damages if a central southern Nepal earthquake would hit. Earthquake resilient buildings are to mitigate the risk and the seismic design of buildings under Nepal National Building Code has been revised and enhanced the regulatory requirements for a new building. On the other hand, the trend of new building structure after the 2015 earthquake has shifted from masonry construction to reinforced concrete (RC) structure, under which trend a construction frequently got different from its design drawings due to lack of awareness and knowledge regarding legal compliance among the building owners and contractors. There are identified issues in the design and building inspection capacity of municipalities, building supervision capacity of architectural engineers, building quality control capacity of contractors, and awareness-raising of related parties. |
| Project Title |
Project for community reconstruction support in the region affected by West Japan’s flooding disaster |
| Country | Japan |
| Client | Peace Winds Japan |
| Period | October 2020 – June 2021 |
| Position |
Project Coordinator |
| Type of Service |
Supporting the people/communities affected by West-Japan floods occurred in 2018 |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Successive heavy downpours hit western Japan in July 2018, causing collapse of eight embankments that led to devastating floods resulting in the loss of 51 lives in Mabi-town, Okayama Prefecture. Immediately after the disaster, Japanese NGO “Peace Winds Japan (PWJ)” provided emergency response, such as rescue activities, material supplies, and assisting for evacuation shelter management in Mabi-town, one of the most affected areas of the disaster. After shifting from emergency period to recovery and reconstruction period, PSD Inc. concluded a secondment contract with the PWJ, and dispatched one employee to the PWJ Soja/Mabi Office from October 2020 to June 2021. |
| Project Title |
Strength regional disaster prevention in disaster-prone area/Strength the capability for disaster prevention and mitigation in the West Japan |
| Country | Japan |
| Client | Peace Winds Japan |
| Period | October 2020 - June 2021 |
| Position |
Project Coordinator |
| Type of Service |
Strengthening the capability of local communities for regional disaster prevention and mitigation |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Japan is one of the most disaster-prone nations due to its particular environmental circumstances, such as geography, geology, and climate. With such conditions, the government’s Earthquake Research Committee (2021) has estimated that Nankai Trough, as the epicenter, will experience magnitude 8-9 class earthquakes with a probability of 70-80% in the next 30 years. Under the circumstances, Peace Winds Japan (PWJ) has implemented various projects to strengthen disaster mitigation and prevention capacities in disaster-prone regions under subsidies from USAID. Given this situation, PSD Inc. concluded a secondment contract with the PWJ, and dispatched one employee to the PWJ Soja/Mabi Office from October 2020 to June 2021. |
| Project Title | Data Collection Survey on Healthcare ICT for Supporting |
||||||||
| Country | World |
||||||||
| Client | ITEC (JICA) |
||||||||
| Period | Mar 2021-Mar 2022 |
||||||||
| Position |
Healthcare Policy |
||||||||
| Type of Service |
the Study for Data Collection | ||||||||
| SDGs |
 |
||||||||
| Photo |
|
||||||||
| Outline |
|
||||||||
| Project Title | Strengthening the Technical Capacity Development of the Local Government Service (Records Management and Fixed Assets Management) The 2nd Phase |
| Country | Ghana |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) |
| Period | July 2021 - February 2022 |
| Position |
Advisor (Local Government Capacity Development) |
| Type of Service |
Independent Expert Service |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | The government system in Ghana has central government institutions and its local government, which structures regions and districts (Metropolitan, Municipal and District). The Office of the Head of the Local Government Service (OHLGS) under the Office of the President has once developed operational manuals both of records management and fixed assets, however, they are not implemented in local government institutions. Many institutions do not completely store important records and update fixed assets registers periodically. |
| Project Title | Project for Improving Continuum of Care for Mothers and Children through the Introduction of Combined MCH Record Book |
| Country | Ghana |
| Client | Ghana Health Service (GHS) |
| Period | April, 2018 to April, 2021 |
| Position |
Project Coordinator |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | In Ghana, the improvement of the health status of mothers and children is considered a high priority. Despite great efforts made to address this issue, the neonatal, and under-five and maternal mortality ratios remain high at 29 per thousand live births, 60 per thousand live births (the 2014 Ghana Demographic and Health Survey (2014 GDHS)), and 319 per 100,000 live births (the Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (MMEIG)), respectively. |
| Project Title | Technical Advice on UHC monitoring and evaluation |
| Country | Kenya |
| Client | World Bank |
| Period | December 2018 – July 2020 |
| Position |
Technical Advisor (Monitoring and Evaluation) |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | ・The Government of Kenya (GoK) is committed towards achieving universal health coverage (UHC) by 2022. In his inaugural speech, the President of the Republic of Kenya announced UHC as a key pillar that the government will deliver during his second term. The renewed political commitment presents a unique opportunity for Kenya to rapidly progress towards UHC. |
| Project Title | Industrial Promotion Project |
| Country | Palestinian Authority |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) |
| Period | March 2019 – March 2022 |
| Position |
Team Leader / Industrial Park Development |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | The Government of Japan has been promoting the regional development through Four Parties’ Consultative Meeting among Israel, Japan, Jordan and Palestine and supporting the economic independence of Palestine as well as mutual trust building since the initiative for “Peace and Prosperity Corridor” was proposed in 2006. JICA has assisted capacity development of PIEFZA (Palestinian Industrial Estates and Free Zones Authority) since 2007, which is responsible Jericho Agro-Industrial Park (JAIP) as the flagship project of the initiative. Up to the end of December 2018, 32 lease agreements were signed, and 13 companies already started operation at Phase I area (11.5 ha). Based on this progress, Japanese Minister of Foreign Affairs, H.E. Mr. Kohno declared in September 2017 that Japan would upgrade “Peace and Prosperity Corridor” initiative. |
| Project Title | Two-Step Loan (TSL) Component of Foreign Direct Investment Promotion Project |
| Country | Bangladesh |
| Client | Bangladesh Bank |
| Period | October 2018 – June 2021 |
| Position |
Project Advisor / Financial Specialist |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | The Government of Bangladesh has identified the diversification of manufacturing industries and the strengthening of export-oriented industries as important issues. This Project aims to improve the investment environment in Bangladesh by improving access to financing opportunities and promoting PPP projects to develop infrastructure including economic zone development. It is consistent with the priority assistance policy of the Government of Japan and JICA. On December 14, 2015, JICA and the Government of Bangladesh signed the loan agreement. |
| Project Title | Verification Survey with the Private Sector for Disseminating |
| Country | Myanmar |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) |
| Period | December 2018 – July 2020 |
| Position |
Chief Adviser |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Foreign direct investment in Myanmar is mainly focused in the low value adding industries, such as garment, because development of supporting industries manufacturing metal and/or plastic parts is not matured. Thus, industrial clustering and sophistication is indispensable for further growth. Proposed EAB may provide the opportunity to gain the technology for develop and process the parts for motor bicycle and automobile with combustion engine. It may also provide the opportunity to study the basic knowledge and technology of electric and electronic parts for future development of electric tricycle and/ or electric four-wheeled vehicles, so that an industrial clustering and sophistication could be achieved. As manufacturing EAB needs labor intensive process, it is believed that international competitiveness can be realized. |
| Project Title | Marketing of medical check-up and smartphone application for behaviour change to control NCDs |
| Country | The Republic of Kenya |
| Client | Africa Scan Inc. |
| Period | March – April 2018 |
| Position |
Technical Adviser |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Through kiosk activities, the Africa Scan, has promoted lifestyle changes in order to control obesity since 2015. In 2017, the Feasibility Survey for Increasing the Uptake of Health Check-ups in Kenya, funded by JICA, was initiated to formulate ODA activity under the JICA PPP (Public-Private Partnership) program. At the same time, Africa Scan was seeking the opportunity to expand its marketing of behaviour change applications in the private sector. Given Kenya’s epidemiological transition to NCDs, it is highly important to promote behaviour change and encourage the practice of regular medical check-ups to control NCDs. |
| Project Title | Data Collection Survey for Universal Health Coverage Promotion Project |
| Country | People’s Republic of Bangladesh |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency |
| Period | August 2017 – February 2018 |
| Position |
Team Leader / Regional Health |
| SDGs |
 |
| Photo |
 |
| Outline | In Bangladesh, the predominant burden of disease has recently shifted from infectious diseases to non-communicable diseases (NCDs). However, referral systems and efforts to promote a healthy lifestyle have not been functioning well in controlling NCDs. At the same time, Bangladesh has experienced a rapid urbanization over the past decade, and the lower income populations in these growing urban areas have not received sufficient quality health services. Based on this situation, the Government of Bangladesh and the Japan International Cooperation Agency agreed to conduct a data collection survey to identify and formulate appropriate JICA activities aimed at achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC). Through discussions with officials of the Government of Bangladesh, development partners, community leaders and other relevant stakeholders, the survey found that it would be important for the control of NCDs to strengthen the referral function from the community level to the secondary level of service providers, and that the primary level of urban health services should be strengthened in order to improve urban health. |
| Project Title | Project for improving maternal and child health services through |
| Country | Republic of Angola |
| Client | Japan International Cooperation Agency |
| Period | May 2017 – June 2018 |
| Position |
Coordinator / Impact evaluation /Training coordination 1 |
| SDGs |
 |
| Outline | Due to decades of colonial rule followed by a prolonged civil war (1975-2002), the Republic of Angola (hereinafter referred to as “Angola”) continues to face multiple socio-economic difficulties. Among these difficulties, ensuring the health of mothers and children is the most pressing need. Poor quality of health services due to a chronic shortage of well-trained health workers and inefficient management of the health system due to the malfunctioning of the referral system have exacerbated the country’s challenging health situation. In response to a request from the government of Angola, ProFORSA |